Introduction
Mixed Reality is revolutionizing the way we interact with content in our usual environment. It opens up new possibilities that we have long thought, only possible in science fiction movies.
Despite its growing popularity, Mixed Reality is still widely subject to confusion. In this first blog post, we will distinguish it from other immersive technologies, in a comprehensible manner. We will then clarify the difference between its marketing, and more complex academic definition. Finally, we will present an overview of the revolutionary possibilities that this technology enables, and the most important hardware existing today in the market.
Introduction
Mixed Reality is revolutionizing the way we interact with content in our usual environment. It opens up new possibilities that we have long thought, only possible in science fiction movies.
Despite its growing popularity, Mixed Reality is still widely subject to confusion. In this first blog post, we will distinguish it from other immersive technologies, in a comprehensible manner. We will then clarify the difference between its marketing, and more complex academic definition. Finally, we will present an overview of the revolutionary possibilities that this technology enables, and the most important hardware existing today in the market.
The established commercial definition
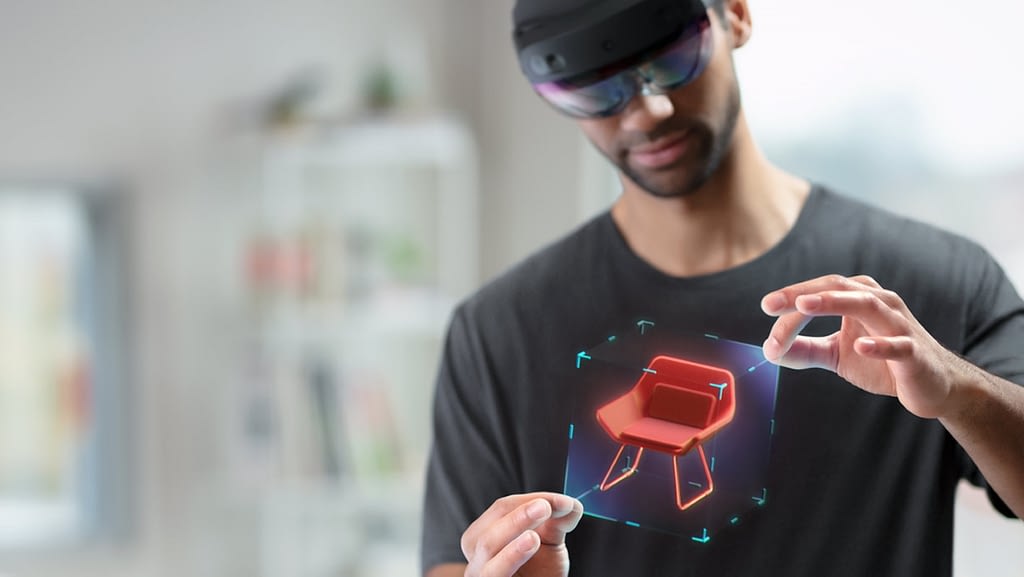

The commercial definition of Mixed Reality (MR) slightly differs from its academic description, and is a little bit more flexible. The major hardware manufacturers define it as a technology that blends your real environment, with virtual content, and enables you to interact with both, in an immersive manner. Some call it spatial computing.
How different is MR from VR and AR?
It is associated with the use of advanced head-mounted glasses, that allow spatial recognition, and advanced interactions such as hand interaction, and eye-tracking. It is also often confused with two other immersive technologies, that are Virtual Reality, and Augmented Reality. What are they exactly?
Virtual Reality (VR) enables a total immersion in virtual environments through the use of headsets. It completely shuts down your physical surrounding.

Augmented Reality (AR) is often associated with mobile phones, or tablets, and enables you to overlay virtual content on top of your physical environment, usually through the use of visual markers. Sometimes Mixed Reality is described as a more advanced version of AR.

The established commercial definition

The commercial definition of Mixed Reality (MR) slightly differs from its academic description, and is a little bit more flexible. The major hardware manufacturers define it as a technology that blends your real environment, with virtual content, and enables you to interact with both, in an immersive manner. Some call it spatial computing.
How different is MR from VR and AR?
It is associated with the use of advanced head mounted glasses, that allow spatial recognition, and advanced interactions such as hand interaction, and eye tracking. It is also often confused with two other immersive technologies: Virtual Reality, and Augmented Reality, that we can simply define as follow:
Virtual Reality (VR) enables a total immersion in virtual environments through the use of headsets. It completely shuts down your physical surrounding.

Augmented Reality (AR) is often associated with mobile phones, or tablets, and enables you to overlay virtual content on top of your physical environment, usually through the use of visual markers. Sometimes Mixed Reality is described as a more advanced version of AR.

The academic definition
The first mention of Mixed Reality goes back to 1994, in an academic paper written by Paul Milgram and Fumio Kishino [1]. It is the most cited paper on AR and VR, up to this date, with over 4800 mentions.
In their paper, Kishino and Milgram defined MR as a spectrum of technologies that involve the merging of real and virtual worlds. They called it the “reality-virtuality continuum” (RV).
The reality-virtuality continuum
In this continuum, any technology that combines real environments, with completely virtual ones belongs to Mixed Reality. Augmented reality is a subcategory of Mixed Reality, while Virtual Reality is excluded, as the opposite reality extreme on the scale.
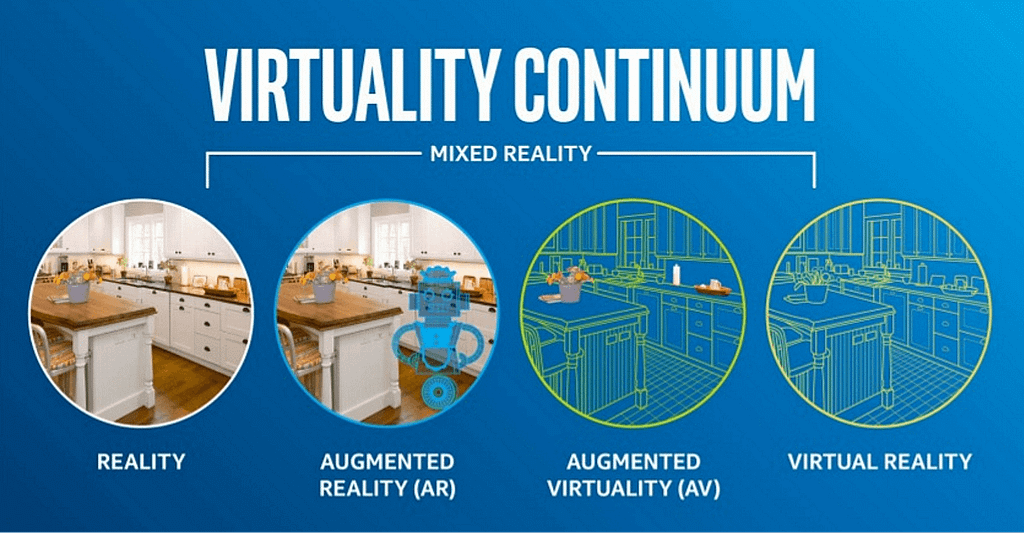
According to this approach, screen-based technologies that overlay 3D content on top of videos, are also considered to be a type of Mixed Reality display, as long as they mix real, and virtual graphics. In comparison, the commercial definition of Mixed Reality – the headset technologies – is much more specific, and only constitute one type of MR technologies along the RV continuum.
Augmented virtuality
Although not popular, this term refers to adding elements of the real world – like hands – to the fully virtual environment of the experience, as opposed to augmented reality.

The academic definition
The first mention of Mixed Reality goes back to 1994, in an academic paper written by Paul Milgram and Fumio Kishino [1]. It is the most cited paper on AR and VR, up to this date, with over 4800 mentions.
In their paper, Kishino and Milgram defined MR as a spectrum of technologies that involve the merging of real and virtual worlds. They called it the “reality-virtuality continuum” (RV).
The reality-virtuality continuum
In this continuum, any technology that combines real environments, with completely virtual ones belongs to Mixed Reality. Augmented reality is a subcategory of Mixed Reality, while Virtual Reality is excluded, as the opposite reality extreme on the scale.

According to this approach, screen-based technologies that overlay 3D content on top of videos, are also considered to be a type of Mixed Reality display, as long as they mix real, and virtual graphics. In comparison, the commercial definition of Mixed Reality – the headset technologies – is much more specific, and only constitute one type of MR technologies along the RV continuum.
Augmented virtuality
Although not popular, this term refers to adding elements of the real world – like hands – to the fully virtual environment of the experience, as opposed to augmented reality.

A taxonomy for Mixed Reality Technologies
In the same paper Milgram and Kishino suggested 3 criteria for distinguishing the different Mixed Reality technologies:
- Extent of World Knowledge (environment and user awareness): it represents the extent to which a device knows about its surrounding environment, and the user, by modeling it through scans. Most mobile AR is very limited in this regard due to its CPU, and GPU. The use of markers for instance gives little, to no information on the environment.
- Reproduction Fidelity (realistic graphics): refers to how realistic is the capture of the real world, and the quality of the rendering.
- Extent of Presence Metaphor (immersion level): translates the level of immersion the user experiences. Depending on technical specifications, some technologies can provide a higher feeling of immersion than others, through realtime imaging, or dimension of the field of view for example.
A taxonomy for Mixed Reality Technologies
In the same paper Milgram and Kishino suggested 3 criteria for distinguishing the different Mixed Reality technologies:
- Extent of World Knowledge (environment and user awareness): it represents the extent to which a device knows about its surrounding environment, and the user, by modeling it through scans. Most mobile AR is very limited in this regard due to its CPU, and GPU. The use of markers for instance gives little, to no information on the environment.
- Reproduction Fidelity (realistic graphics): refers to how realistic is the capture of the real world, and the quality of the rendering.
- Extent of Presence Metaphor (immersion level): translates the level of immersion the user experiences. Depending on technical specifications, some technologies can provide a higher feeling of immersion than others, through realtime imaging, or dimension of the field of view for example
The field of view
One of the most important aspects of immersion in Mixed Reality experiences is the field of view. The diagonal FOV on the leading devices is around 50 diagonal degrees.
The size, and placement of virtual objects according to the FOV, play a major role in defining how immersive the designed experiences are.
The field of view
One of the most important aspects of immersion in Mixed Reality experiences is the field of view. The diagonal FOV on the leading devices is around 50 diagonal degrees.
The size, and placement of virtual objects according to the FOV, play a major role in defining how immersive the designed experiences are.
The most important Mixed Reality headsets in the market

Magic Leap 1
Price: starting from 2,295 $
Resolution: 1K per eye
The diagonal field of view: 50°
Weight (glasses): 316g
CPU: 2 Denver 2.0 64-bit cores +
4 ARM Cortex A57 64-bit cores
GPU: NVIDIA Pascal™, 256 CUDA
cores Graphic
Memory: 8GB
Storage: 124GB
Battery life: up to 3 hour

Hololens 2
Price: starting from 3,500$
The diagonal field of view: 52°
Resolution: 2K per eye
Weight: 566g
Processing unit: Qualcomm
Snapdragon 845
Memory: 4GB
Storage: 64GB
Battery life: up to 3 hours

Nreal
Price: starting from 499$
The diagonal field of view: 52°
Resolution: 1K per eye
Weight: 88g
Processing unit: Qualcomm
Snapdragon 845
Battery life: up to 3 hours
Two B2B leaders and one B2C pioneer
All 3 devices are well equipped with sensors, to provide a great environment, and user awareness. For instance, through cameras, depth sensors, hand and eye-tracking, and mics.
When it comes to immersion levels, Magic leap 1, and Hololens 2 are the most powerful headsets with their advanced tracking. They are oriented to B2B use cases, and are the best in the market in this category.
Nreal is the most important B2C oriented Mixed Reality headset. The glasses support USB C, and can be directly plugged to mobile phones to showcase content, or to its provided external processing unit, if desired
The most important Mixed Reality headsets in the market

Magic Leap 1
Price: starting from 2,295 $
Resolution: 1K per eye
The diagonal field of view: 50°
Weight (glasses): 316g
CPU: 2 Denver 2.0 64-bit cores +
4 ARM Cortex A57 64-bit cores
GPU: NVIDIA Pascal™, 256 CUDA
cores Graphic
Memory: 8GB
Storage: 124GB
Battery life: up to 3 hours

Hololens 2
Price: starting from 3,500$
The diagonal field of view: 52°
Resolution: 2K per eye
Weight: 566g
Processing unit: Qualcomm
Snapdragon 845
Memory: 4GB
Storage: 64GB
Battery life: up to 3 hours

Nreal
Price: starting from 499$
The diagonal field of view: 52°
Resolution: 1K per eye
Weight: 88g
Processing unit: Qualcomm
Snapdragon 845
Battery life: up to 3 hours
Two B2B leaders and one B2C pioneer
All 3 devices are well equipped with sensors, to provide a great environment, and user awareness. For instance, through cameras, depth sensors, hand and eye-tracking, and mics.
When it comes to immersion levels, Magic leap 1, and Hololens 2 are the most powerful headsets with their advanced tracking. They are oriented to B2B use cases, and are the best in the market in this category.
Nreal is the most important B2C oriented Mixed Reality headset. The glasses support USB C, and can be directly plugged to mobile phones to showcase content, or to its provided external processing unit, if desired
A revolution in Human-Machine-Environment interactions
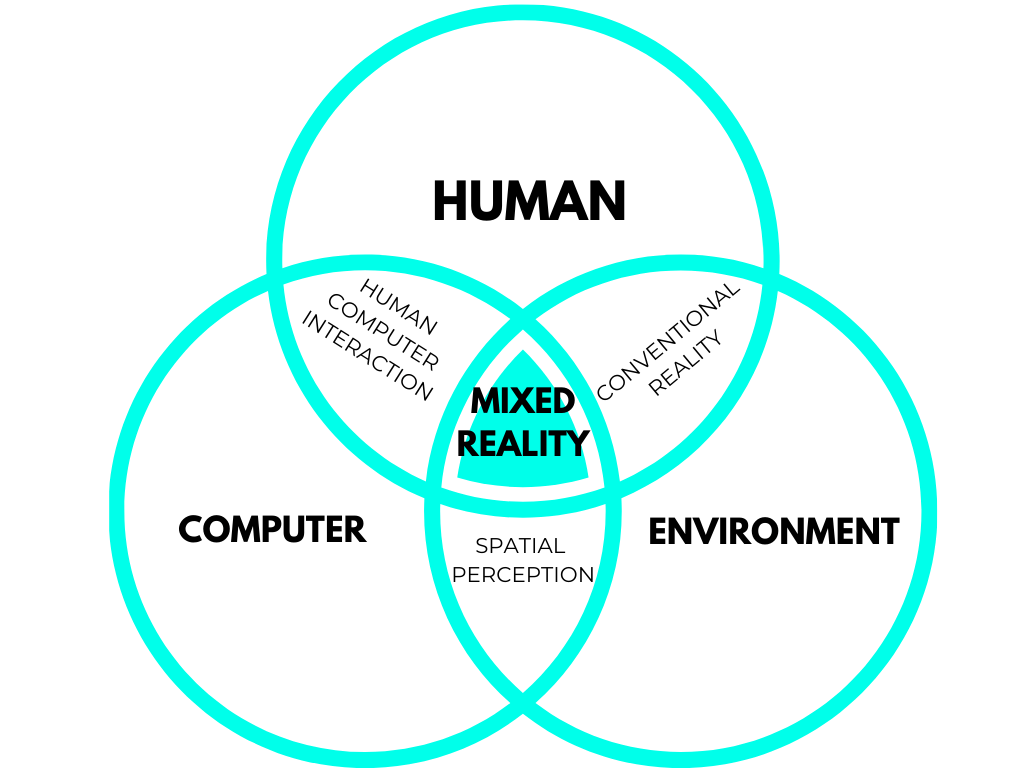
Computers, and smartphones revolutionized the way we access data. It takes one or a few clicks to get almost any information. Yet, we are still constrained to look into our screens to view information about the world we live in. Mixed Reality enables you to view data directly in the real world, and offers unprecedented ways to interact with it.
A revolution in Human-Machine-Environment interactions

Computers, and smartphones revolutionized the way we access data. It takes one or few clicks to get almost any information. Yet, we are still constrained to look into our screens to view information about the world we live in. Mixed Reality enables you to view data directly in the real world, and offers unprecedented ways to interact with it.
Current and future technologic possibilities
What Mixed Reality allows now
Here are some of the current possibilities that the current devices allow software development to perform.
- Placing 3D content in the space
- Placing 3D screens and media in a conventional space
- Space meshing
- Hand tracking
- Eye-tracking
- 3D sound
- Multiuser experiences
Some of the most awaited next possibilities for MR include:
- 5G integration to allow the instantaneous synchronization of important data volumes, particularly when used with IoT.
- Connectivity with mobile phones as Nreal allows. This will open more application possibilities, especially in B2C.
- A more intuitive user awareness through advanced hand, and eye-tracking, voice recognition, and even neural activity in the upcoming years.
- A more important field of view, and resolution to allow hybrid devices: switching between VR and MR at will.
Current and future technologic possibilities
What Mixed Reality allows now
Here are some of the current possibilities that the current devices allow software development to perform.
- Placing 3D content in the space
- Placing 3D screens and media in a conventional space
- Space meshing
- Hand tracking
- Eye-tracking
- 3D sound
- Multiuser experiences
Some of the most awaited next possibilities for MR include:
- 5G integration to allow the instantaneous synchronization of important data volumes, particularly when used with IoT.
- Connectivity with mobile phones as Nreal allows. This will open more application possibilities, especially in B2C.
- A more intuitive user awareness through advanced hand, and eye tracking, voice recognition, and even neural activity in the upcoming years.
- A more important field of view, and resolution to allow hybrid devices: switching between VR and MR at will.
Conclusion
- The established commercial definition of Mixed Reality is very flexible and refers to headset devices that are able to blend the real environment with virtual 3D graphics, in a way that enables users to interact with both, in a realistic and immersive way.
- Mixed Reality was first mentioned in a research paper, back in 1994. This academic definition is still the more cited in research until now, and is also more rigorous, and complex the commercial one. It considers any display technology mixing real with virtual content, as belonging to the Mixed Reality continuum.
- Mixed Reality is revolutionizing our access to data, as it enables us to view it directly in the conventional reality, instead of relying on screens as intermediaries. Its biggest potential is yet to come with 5G, advancements in FOV’s, and intuitive user awareness.
References
[1] Milgram, P., & Kishino, F. (1994). A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE TRANSACTIONS on Information and Systems, 77(12), 1321–1329.
[2] Dieter Bohn. “MICROSOFT’S HOLOLENS 2: A $3,500 MIXED REALITY HEADSET FOR THE FACTORY, NOT THE LIVING ROOM” TheVerge, February 24, 2019, https://www.theverge.com/2019/2/24/18235460/microsoft-hololens-2-price-specs-mixed-reality-ar-vr-business-work-features-mwc-2019
[2] MarK Billinghurst. “What is Mixed Reality?” Medium, Mars 31, 2017, https://medium.com/@marknb00/what-is-mixed-reality-60e5cc284330
[3] Maria Nova, “4R’s or get your head around Virtuality Continuum” Medium, February 13, 2018, https://medium.com/@Maria_Nova/4rs-or-get-your-head-around-virtuality-continuum-625e256ddd1d
[4] Magic Leap. (2018). All Fact sheets. Retrieved from https://www.magicleap.com/static/magic-leap-fact-sheet.pdf
[5] Microsoft. (2019). Hololens 2 pricing and options. Retrieved from https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens/buy
[6] Nreal. (2019). Specs. Retrieved from https://www.nreal.ai/specs/
References
[1] Milgram, P., & Kishino, F. (1994). A taxonomy of mixed reality visual displays. IEICE TRANSACTIONS on Information and Systems, 77(12), 1321–1329.
[2] Dieter Bohn. “MICROSOFT’S HOLOLENS 2: A $3,500 MIXED REALITY HEADSET FOR THE FACTORY, NOT THE LIVING ROOM” TheVerge, February 24, 2019, https://www.theverge.com/
2019/2/24/18235460/microsoft-hololens-2-price-specs-mixed-reality-ar-vr-business-work-features-mwc-2019
[2] MarK Billinghurst. “What is Mixed Reality?” Medium, Mars 31, 2017, https://medium.com/@marknb00/what-is-mixed-reality-60e5cc284330
[3] Maria Nova, “4R’s or get your head around Virtuality Continuum” Medium, February 13, 2018, https://medium.com/@Maria_Nova/4rs-or-get-your-head-around-virtuality-continuum-625e256ddd1d
[4] Magic Leap. (2018). All Fact sheets. Retrieved from https://www.magicleap.com/static/magic-leap-fact-sheet.pdf
[5] Microsoft. (2019). Hololens 2 pricing and options. Retrieved from https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens/buy
[6] Nreal. (2019). Specs. Retrieved from https://www.nreal.ai/specs/
